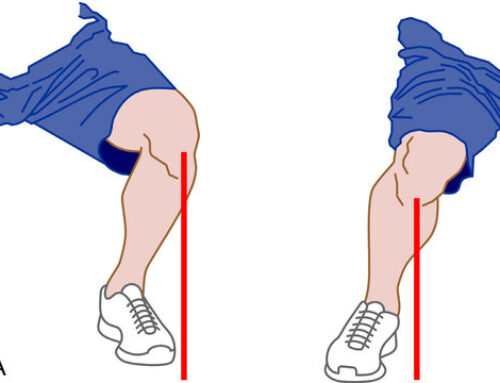
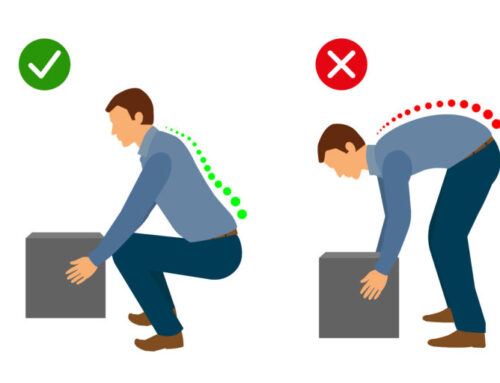
What is the spinal canal stenosis?
Spinal canal stenosis is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine that can put pressure on the nerves that run down the spine. It occurs most often in the lower back and neck.
Types of spinal canal stenosis
They are classified according to the region of the spine in which occurs. It is possible to have more than one type. The two main types of spinal stenosis are:
Cervical stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the neck portion of the spine.
Lumbar stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the lower back part of the spine. It is the most common form of spinal stenosis.
Symptoms
Many people have evidence of spinal stenosis on MRI or CT scans, even though they have no symptoms. When symptoms begin to appear, they appear gradually and worsen over time. The symptoms depends on the location of the stenosis and the affected nerves.
In the neck (cervical spine)
In the lower back (lumbar spine)
MRI and CT scans can measure the canal diameters and confirm the diagnosis.
Consult your doctor if you have any of the symptoms listed. It is important to perform a complete medical history review and do an evaluation of the patient, in addition to physical and neurological examinations. The patient should report their symptomatology completely, from the beginning to the final evolution.
Spinal canal stenosis is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine that can put pressure on the nerves that run down the spine. It occurs most often in the lower back and neck.
Types of spinal canal stenosis
They are classified according to the region of the spine in which occurs. It is possible to have more than one type. The two main types of spinal stenosis are:
Cervical stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the neck portion of the spine.
Lumbar stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the lower back part of the spine. It is the most common form of spinal stenosis.
Symptoms
Many people have evidence of spinal stenosis on MRI or CT scans, even though they have no symptoms. When symptoms begin to appear, they appear gradually and worsen over time. The symptoms depends on the location of the stenosis and the affected nerves.
In the neck (cervical spine)
In the lower back (lumbar spine)
MRI and CT scans can measure the canal diameters and confirm the diagnosis.
Consult your doctor if you have any of the symptoms listed. It is important to perform a complete medical history review and do an evaluation of the patient, in addition to physical and neurological examinations. The patient should report their symptomatology completely, from the beginning to the final evolution.